More than 10% of the U.S. population has diabetes (more than 34 million Americans), and it is estimated that many more (88 million U.S. adults) have prediabetes. Diabetes is considered a chronic disease, and if not treated, can have deadly complications. Today, diabetes is the seventh leading cause of death in the United States.
Although there is no cure for diabetes, the early stages of Type 2 Diabetes (T2D) – or “prediabetes” – can be reversed. When detected early, both prediabetes and diabetes can have hopeful health outcomes. November is Diabetes Awareness Month – a time to recognize diabetes risk for early detection and intervention.
What is prediabetes?
Prediabetes is characterized by having higher-than-normal blood sugars, but not high enough to be diagnosed as diabetes. Although “pre” diabetes doesn’t sound like a big deal, it is considered a serious health condition that increases risk for developing T2D, heart disease and stroke. There are many risk factors for prediabetes, including age, genetics and physical inactivity.
Prediabetes exists on the same continuum as T2D, and if unaddressed, could develop into T2D within five years, according to the CDC. Most people live with prediabetes well before they develop T2D, posing a critical opportunity to intervene and change the course of the disease before it becomes more serious. Small lifestyle changes can have a huge impact on delaying or preventing diabetes altogether. When prediabetes becomes T2D, it cannot be cured, but early detection remains critical to prevent complications.
How do I know if I have prediabetes?
Prediabetes often does not have clear symptoms, which is why it can be overlooked for years. Of those with prediabetes, 8 out of 10 don’t know they have the condition.
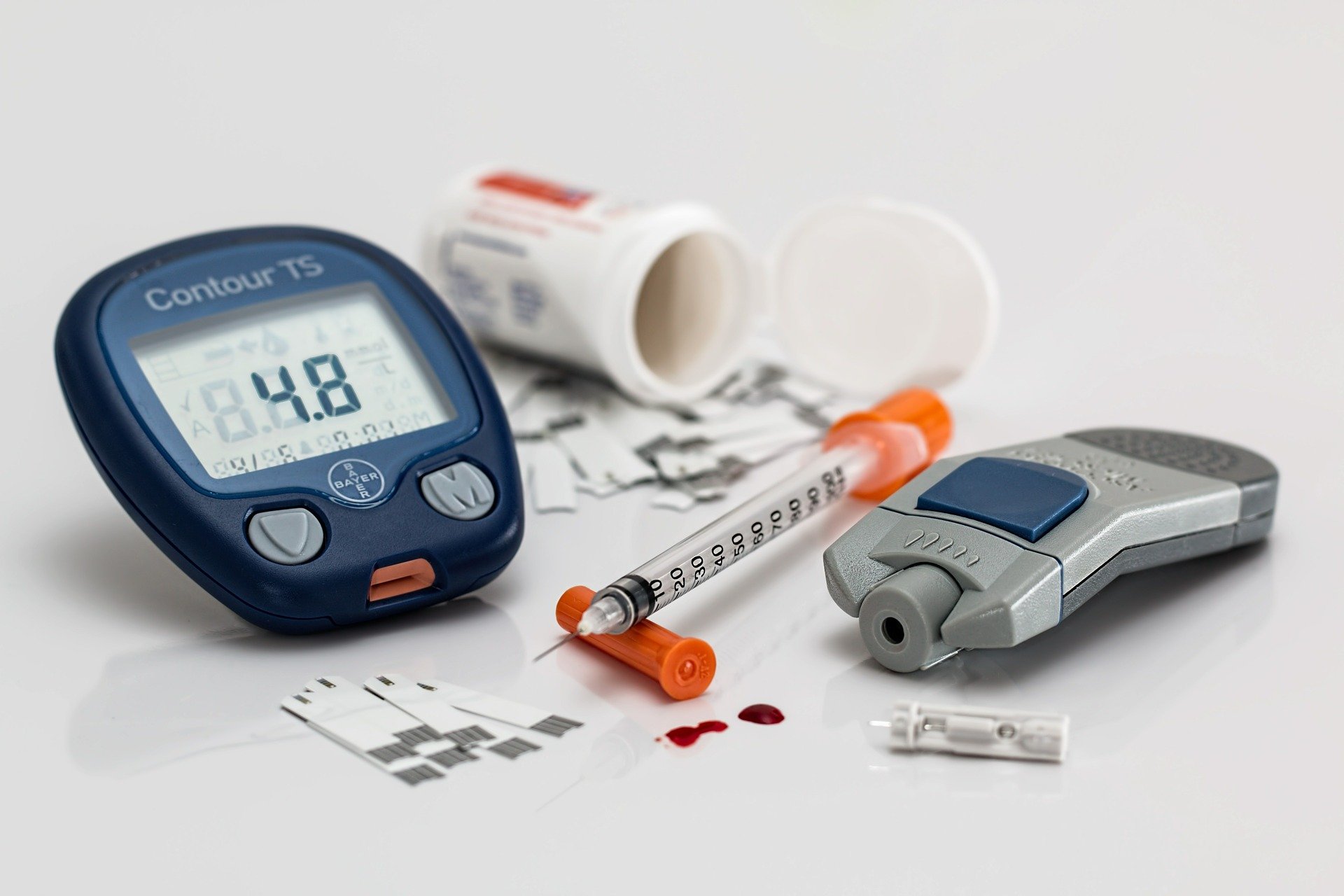
You can get a simple blood sugar test to find out if you have prediabetes. Ask your doctor to get a “Glycated Hemoglobin (A1C) test”, which indicates your average blood sugar for the past two to three months. Think of a fasting blood glucose test like a single baseball game — this tells you about your blood sugars just in that moment of time. An A1C is much more like a batting average for the whole season — what blood sugars have looked like for the past few months. In general, an A1C level between 5.7% and 6.4% is considered prediabetes. A1C levels at 6.5% or higher are considered in the diabetes range. If you have diagnosed diabetes, work with your health care provider to establish a goal for your A1C.
What can I do to prevent diabetes?
Proper nutrition, physical activity, stress management, weight management and sleep hygiene can help keep prediabetes from developing into T2D.
It can be challenging to navigate lifestyle changes on your own. The National Diabetes Prevention Program at CSU’s Kendall Reagan Nutrition Center provides resources and support for making those lifestyle changes to lower your diabetes risk. NDPP helps participants practice healthy eating and regular physical activity. Classes are led by KRNC certified lifestyle coaches who are also master’s-level registered dietitians.
KRNC is offering its next session of the yearlong NDPP starting Jan. 22, 2021. If qualified, your health insurance may cover the entire cost of the program. CSU employees not covered by their insurance will receive a 50% discount on registration thanks to Commitment 2 Campus. Students also receive a 50% discount.
For those with diagnosed diabetes, KRNC also offers its 8-week Diabetes Empowerment nutrition-focused cooking program. This program provides the comprehensive information and hands-on cooking to help manage diabetes. Join our interest list at colostate.az1.qualtrics.com/jfe/form/SV_6SfURan5SMJ0sYt to get notifications for our next offering.
For more information, call (970) 495-5916 or email nutritioncenter@colostate.edu.
Take this 1-minute quiz to know your diabetes risk: www.cdc.gov/diabetes/risktest/index.html